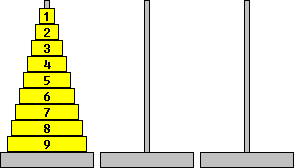







This puzzle consists of three pegs, and a stack of circular disks of differing sizes, each of which can be threaded onto a peg. At the start, the disks are all in order on the first peg, from the largest disk at the bottom to the smallest disk at the top. You are only allowed to move one disk at a time from one peg to another, and at no time may a disk be placed on top a smaller disk. The aim of the puzzle is to move all the disks from the first peg to the third. The puzzle can be solved with any number of disks, but it takes longer with more disks.
This puzzle was invented by the French mathematician Edouard Lucas in 1883. The description included with the puzzle when it was originally sold called it a simplified version of a mythical 'Tower of Brahma' in a temple in the Indian city of Benares. This tower consisted of 64 disks of gold, which had to be moved to another position by priests. The legend went that before they complete the task, the temple would crumble into dust and the world would vanish in a clap of thunder.
 Rudenko Matryoshka is a version of the standard Hanoi puzzle where the moving
pieces are like traditional nested Matryoska dolls, with the outer shells
being analogous to the smaller disks. The pieces are constrained to move
along a track, and there is a locking mechanism is place that is supposed
to prevent more than one piece moving at the same time.
Rudenko Matryoshka is a version of the standard Hanoi puzzle where the moving
pieces are like traditional nested Matryoska dolls, with the outer shells
being analogous to the smaller disks. The pieces are constrained to move
along a track, and there is a locking mechanism is place that is supposed
to prevent more than one piece moving at the same time.
 Rudenko Clips is clever version of the Hanoi puzzle. Its body has a horizontal
bar onto which are hung a set of concentric bands. The bar has three sections,
and you can move a band from one section to an adjacent one. You can only move
the outer band of a section, and can only move it if it is larger than all the
bands on the section you move it to. This is slightly more restrictive than the
standard Hanoi rules, since you cannot move a band directly between the outer
sections but only via the middle section. This means that only the largest band
can be moved in one move between the outer sections, while all other bands have
to do it in two steps.
Rudenko Clips is clever version of the Hanoi puzzle. Its body has a horizontal
bar onto which are hung a set of concentric bands. The bar has three sections,
and you can move a band from one section to an adjacent one. You can only move
the outer band of a section, and can only move it if it is larger than all the
bands on the section you move it to. This is slightly more restrictive than the
standard Hanoi rules, since you cannot move a band directly between the outer
sections but only via the middle section. This means that only the largest band
can be moved in one move between the outer sections, while all other bands have
to do it in two steps.
 Rudenko Disk is a disc-shaped version of the puzzle where the moving pieces
are beads constrained to move along a track. The pegs are represented by the three
connected dead-end tracks. The pieces cannot move further down each track than their
starting location. This is slightly less restrictive than the standard Hanoi rules,
as it does not restrict the size of the pieces stacked on top of another, only
hoe many can be stacked on it.
Rudenko Disk is a disc-shaped version of the puzzle where the moving pieces
are beads constrained to move along a track. The pegs are represented by the three
connected dead-end tracks. The pieces cannot move further down each track than their
starting location. This is slightly less restrictive than the standard Hanoi rules,
as it does not restrict the size of the pieces stacked on top of another, only
hoe many can be stacked on it.
Note that the Panex puzzle has a similar rule, but
as that puzzle has two towers that need to be exchanged, it is much harder.
If your browser supports JavaScript, then you can play the Towers of Hanoi by clicking the link below:
If the disks are placed on the pegs one by one, starting with the largest one, then there are always three choices when placing a disk. Any legal position can be constructed in this manner. There are therefore 3N positions for N disks. At each position (except when all the disks are on one peg) there are 3 possible moves, one which brings you closer to the start, one which brings you closer to the end, and one which brings you closer to having all disks on the middle peg.
The Rudenko disk has more possible positions, but it is very hard to calculate exactly how many.
The puzzle can be solved by a recursive algorithm. To move a stack of N disks from one peg to another, simply follow the following steps:
This method works because this reduces the puzzle of N disks to a puzzle of only N-1 disks. That in turn is reduced to a puzzle of N-2 disks, and so on until the puzzle is reduced to moving a stack containing only 1 disk, which is easy. This algorithm has exactly 2N-1 moves, because from the steps above it is easily seen that Length(N) = 2·Length(N-1) + 1, and Length(1) = 1, and the result then follows by induction. This solution is also minimal, in other words there is no shorter way to solve it, because every solution for N disks must reach the intermediate position with the top N-1 disks on the spare peg.
The recursive algorithm works very well, but in practice there are several rules of thumb which can guide you:
There are 3N possible positions, and 2N positions are encountered while solving the puzzle directly using the methods above. All the other 3N-2N positions break the odd/even rules by having two disks of the same parity on top of each other (or the largest disk on the middle peg). The odd/even rule always rules out one of the three available moves, so that you can only go forwards to the end or back to the beginning.
If you stop in the middle of solving and forget what your last move was, then you may find yourself reversing previous moves and ending up back at the beginning. The rules of thumb also do not help you when you encounter one of the 3N-2N positions that do not lie on the direct route between the start and the end. In these cases the correct move can be deduced as follows:
This is best illustrated by example:
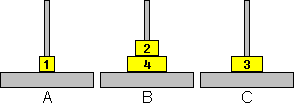
Here we want to move disk 4 from peg B to peg C. This means that we need
all the smaller disks to be on peg A, so we must move disk 3 from peg C to
peg A first. For this we need all disks smaller than 3 to be on peg B. Disk
2 is already on peg B, but disk 1 is not so this has to be moved to peg B.
The correct move is therefore disk 1 from A to B.
Similarly if we want to move back to start, to move disk 4 from B to A means
that disk 3 and smaller must be on peg C. Disk 3 is already on C, so we must
put disk 2 on C next. Disk 1 does not obstruct this, so the correct move is
disk 2 from B to C.
If we wanted all the disks on peg B instead, then the correct move would be
move disk 1 from A to C. Note that this move does break the odd/even rule
(disk 1 moves on top of disk 3), but that is only because the position itself
already breaks that rule (disk 2 lies on disk 4).
An interesting pattern emerges if you map out all possible positions in a graph, with lines connecting two positions that differ by a single move. The graph will resemble of Sierpinski's gasket; the more disks, the more closely its graph approximates the gasket's fractal triangular shape. The shortest solution is the path along the edge of the triangle, from one corner to the other.
This puzzle can be solved recursively in a similar way to the standard Hanoi puzzle, except that it has a few more steps. To move a set of N bands from the middle section to the left section, you can follow the following steps:
From these steps it is easy to see that Length(N) = 3·Length(N-1) + 1 and Length(1) = 1. It can then be proved by induction that this algorithm takes exactly (3N-1)/2 moves. This solution is also optimal.
Rudenko Clips has 7 moving pieces, so the number of moves needed to move all of them to or from the middle section is (37-1)/2 = 1093.
At any point in the middle of the solution, there are only two moves possible - moving the large band from one side to the other, or moving the second largest accessible piece. You can deduce what the next move is by looking at the smallest band that is not yet solved, determining how it needs to be moved, and deducing what conditions this imposes on the next larger band. Then use the same reasoning on that band, and so on until you get to a band that can be moved.
We can map out the positions in a graph in the same way as before. Instead of a Sierpinski's gasket, we now get a single line going through all 3N positions. In every triangle in the original graph, (the middle of) one of the three sides represents a long move between the outer pegs. These have been removed leaving only a single fractal-like path.
The standard Hanoi solution can be applied to this puzzle. It has 7 moving pieces, so it takes 27-1 = 127 moves if solved in this way. It is however possible to take advantage of the fact that it is less restricted than the normal Hanoi puzzle. For example, a four disk puzzle can be solved in 13 moves instead of 15 as follows:
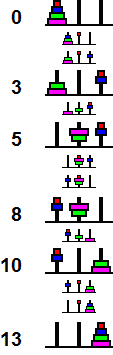
The shortcut above generalises, and allows you to reduce the problem of moving a stack of N disks to the simpler problems of moving a stack of N-2 disks three times, and moving the two largest disks twice. This leads to a solution for which the length satisfies the equality Length(N) = 3·Length(N-2) + 4. From this and the fact that Length(1) = 1, and Length(2) = 3, we can prove by induction that if N is even, say N=2n, then Length(2n) = 5·3n-1 - 2, and if N is odd, N=2n-1, then Length(2n-1) = 3n - 2.
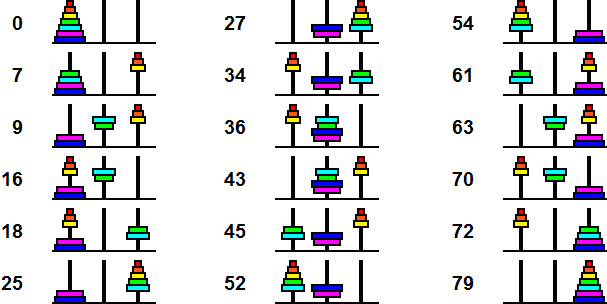
I believe that it is impossible to do better than the above solution whatever the size of the puzzle. I have verified this by computer up to N=10 disks, but not proven it mathematically. The following table shows the results for various sizes of this puzzle.
| Standard Hanoi | Rudenko Disk | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of disks | Solution Length | Number of positions | Optimal Solution Length | Number of Optimal Solutions | Number of positions | Diameter | Antipodes |
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |
| 2 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 3 | |
| 3 | 7 | 27 | 7 | 2 | 33 | 8 | |
| 4 | 15 | 81 | 13 | 1 | 141 | 17 | |
| 5 | 31 | 243 | 25 | 8 | 693 | 33 | |
| 6 | 63 | 729 | 43 | 1 | 3813 | 59 | |
| 7 | 127 | 2187 | 79 | 512 | 22797 | 107 | |
| 8 | 255 | 6561 | 133 | 1 | 144213 | 187 | |
| 9 | 511 | 19683 | 241 | 134217728 | 947853 | 335 | |
| 10 | 1023 | 59049 | 403 | 1 | 6396837 | 570 | |